
Morgan Stanley IM: No Easy Fix
The conundrum faced by central banks continues as they seek to control inflation, at the risk of pushing economies into recession. The Global Balanced Risk Control team discuss the investment implications and tactical allocations to navigate this complex environment.
12.09.2022 | 08:20 Uhr
Here you can find the complete article
After a sustained rally over the summer, both the U.S and Europe sold off, with the S&P 500 (TR) (USD) down 4.1% and MSCI Europe (TR) (EUR) -4.9%1. Japanese equities appear to offer some defensiveness, as the MSCI Japan (TR) (JPY) returned 1.1%1. The MSCI Emerging Markets Index (USD) returns also proved more defensive, marginally up 0.5%1. Energy was once more the top performing sector over the month, as the MSCI ACWI Energy (USD) returned 2.4%1. However, after much of the year significantly above $100 a barrel, there was some relief as oil finally moved below this, with WTI ending the month $90.1bbl and Brent $96bbl1. As markets sold off, the VIX index began creeping back up, reaching 26 by month end2.
The selloff can partly be attributed to the continuing conundrum faced by central banks, including the Federal Reserve (the Fed), European Central Bank (ECB) and the Bank of England (BoE). They must hike enough to control inflation, but with the risk of pushing their economies into a recession. At Jackson Hole, Federal Reserve Chairman, Jerome Powell re-iterated the Fed’s hawkish resolve, stating that even if softening labour markets and slower growth were to bring some pain, “failure to restore price stability would mean far greater pain”3.
Hard landing in the U.S.?
However, there are a number of factors which could help the U.S. avoid a hard landing in 2022. Capital expenditure (capex) is better supported compared with previous cycles, given healthy credit demand. Pent-up demand and the need for energy investment should also support capex. Capex may be front-loaded too, as the tax advantage of depreciating 100% in one year – part of Trump’s Tax Cuts and Jobs Act 2017 - starts to decrease annually from 2023. Moreover, though U.S. consumers are seeing inflation erode their personal income in real terms and savings rates have fallen to their lowest level since 2008 (i.e. from a pandemic high of 26% to 5.1%4, they still have a higher stock of personal savings compared to pre-pandemic levels, which can cushion spending. Whilst consumers are leveraging up, again this is not as pronounced as previous cycles, since leverage levels have been in decline since 2008’s Global Financial Crisis. The housing market, despite its current strength, is one of the main vectors which could help the Fed bring inflation under control, given mortgages’ sensitivity to rate rises.
That said, if inflation does not come down the Fed may have to act more aggressively than market participants currently anticipate, to prevent it becoming entrenched. Combine this with the time it takes for hikes to take effect, if it then turns out that the policy is too aggressive, it may be too late for the Fed to reverse its actions and avoid a hard landing.
The long winter
We are in an energy crisis caused by supply shortages. Therefore, government measures to cushion the blow to consumers are likely to support demand, in turn leading to higher prices, in a self-defeating cycle. As high energy prices exacerbate inflation, the only way central banks can act is by supporting currencies and suppressing activity enough to avoid an entrenchment of inflationary expectations. In this context, Europe is lagging in its hiking cycle and has a higher exposure to Russian gas supply, so may be more vulnerable to recessionary risks. Whilst the region has for now been able to remain on track to achieve its storage fill targets through gas supplies from UK pipelines, as we move into winter, this could come under pressure as temperatures drop. Unless supply is restored, only demand destruction can resolve the demand-supply mismatch. Again, there is no easy solution to this conundrum.
Investment implications
We maintain a cautious equity exposure and reduced duration in light of the increasing pressure on Central Banks to prevent inflation expectations from de-anchoring. Against this backdrop, we made the following tactical changes to our views:
U.S. 10-Year Treasuries
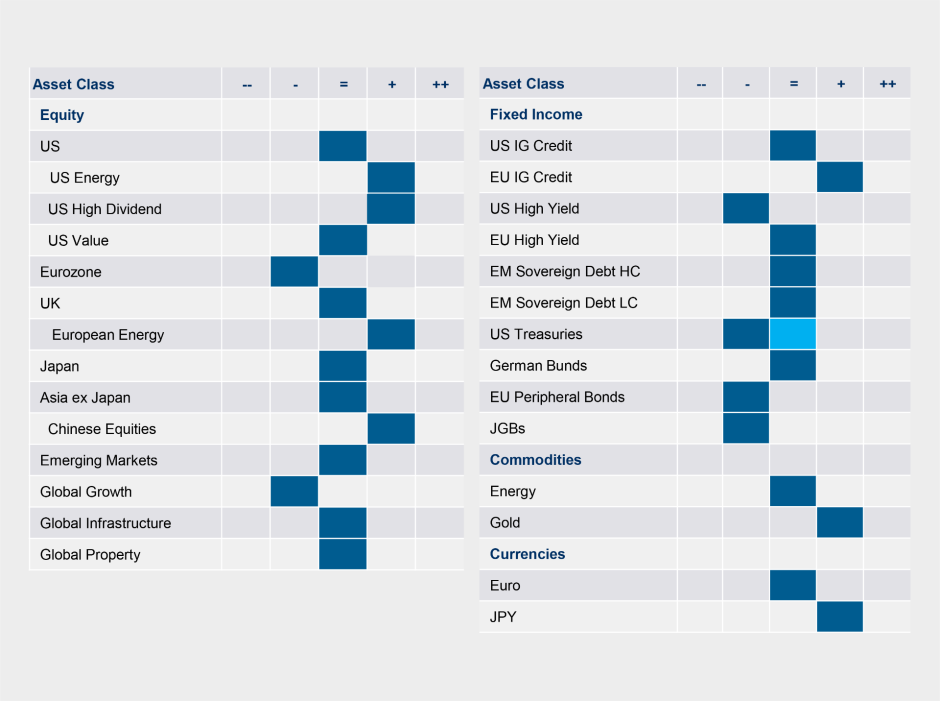
We moved from neutral to underweight U.S. 10-Year Treasuries, moving to short-dated T-Bills to reduce duration.
U.S. High Yield
We increased our underweight to U.S. High Yield and added to our short-dated T-Bills. Recently, U.S. High Yield spreads have tightened significantly, with many market participants forecasting the Fed will soon reach the terminal rate and rate cuts should commence in 2023, with economic growth remaining positive. In contrast, we believe these scenarios are mutually exclusive and look for a higher terminal rate and no significant cuts to the Fed funds rate in 2023, unless there is a deep recession in the U.S.. U.S. High Yield remains expensive compared to U.S. Investment Grade, but this pricing should turn as Fed tightening impacts lower quality borrowers negatively.
The index performance is provided for illustrative purposes only and is not meant to depict the performance of a specific investment. Past performance is no guarantee of future results. See Disclosure section for index definitions.
Tactical Positioning
We have provided our tactical views below:




Diesen Beitrag teilen: